Lesson 3: Debugging with Serial
Table of Contents
- Using Serial.print for debugging
- Modify your blink code to use Serial.print
- Use the built-in LED
- Next Lesson
Video. A video showing how to use Serial.println() to debug code. For this, we modified the simple blink program to add serial prints (source code).
Debugging code is always hard. Debugging code+circuits is even harder! 💪🏽 Though we’re only on our third Arduino lesson (woohoo!), it’s time to introduce some Arduino debugging strategies.
For hardware debugging, multimeters and oscilloscopes are useful. We realize that many of you may not (yet) have your own multimeters or oscilloscopes. In this case, we recommend building your circuits in a simulation tool like Tinkercad Circuits and using their virtual instruments (e.g., multimeters). If you’re physically building something and it’s not working, you could try to replicate it in Tinkercad or some other simulation tool.
For code debugging, it’s common to use “printline” statements (yes, I know! 🤣)—see video above. Currently, the Arduino IDE does not support code debugging (e.g., breakpoints, code stepping, memory stack dumps); however, there is rudimentary debugging support (e.g., stepping through code) in Tinkercad Circuits.
With the introduction of the Arduino IDE 2.0, there is debugging support; however, only certain Arduino boards are supported and you need specialized hardware.
Using Serial.print for debugging
Using “print out” statements to “console” is perhaps the oldest (and possibly most robust) debugging technique. It is the standard technique for Arduino as well (although can be tedious at times).
Unlike JavaScript, Java, C# or other code that runs in your web browser or natively on your desktops/laptops, your Arduino code is running on the Arduino’s microcontroller (e.g., the Uno uses the ATmega328P; the Leonardo uses the ATmega32u4). Thus, when we “print to console”, we actually need to get the data from the Arduino’s microcontroller on to your development computer. For this, Arduino uses the serial protocol. More specifically, the function Serial.print() and Serial.println().
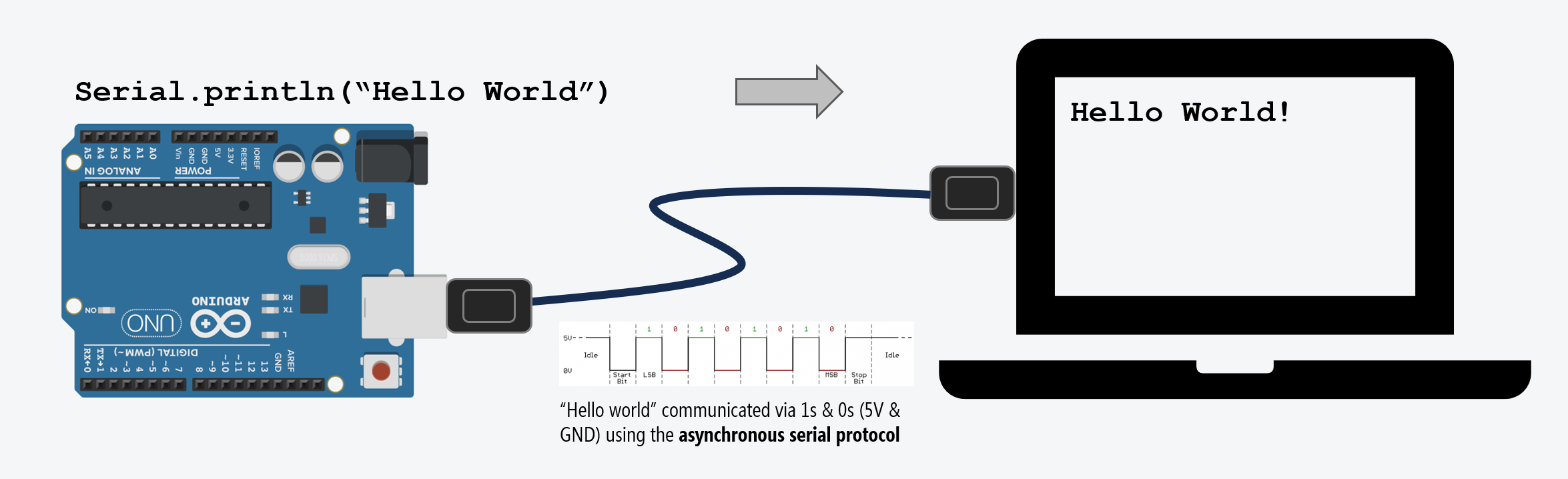
These two functions print data to the serial port as human-readable ASCII text (the println version simply inserts a carriage return \r followed by a newline character \n). To send data without converting it to ASCII text, you need to use Serial.write().
In later lessons, we’ll see how to use serial communication for more than just debugging purposes but to actually bidirectionally communicate with the computer (see L1: Intro to Serial and these ITP examples). For our introductory lessons, however, we’ll just use it to print out information about how our program is performing.
Once you turn on serial (via
Serial.begin()), you can no longer use digital Pins 0 or 1 for I/O because these pins are used for serial communication (digital pin 0 is RX and pin 1 is TX). See Arduino documentation.This is why many of our “starter” examples use Pin 3 rather than Pins 0 or 1 (Pin 3 also has the added benefit of being configurable for analog output, which we’ll get to in the next lesson).
Build a simple “Hello World!” Serial.print program
Let’s build a simple “Hello World!” program that uses Serial.print functionality to receive ASCII data over the serial port. We don’t even need external hardware for this: just our Arduino Leonardo and a USB cable.
Step 1: Initialize the serial port
To use the serial port, we must first initialize it with Serial.begin(BAUD_RATE). The baud rate is the transmission speed in bits per second (bps) and is typically set to 9600 unless greater speeds are needed. Because the Serial library uses asynchronous communication, both the transmitter and receiver need to agree on the speed of communication (the baud rate). So, you will also have to set the baud rate in the “Serial Monitor” window (see Step 3 below).
Typically, we initialize the serial port in setup(), as it only needs to run one time.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // opens serial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
}
void loop() {}Step 2: Use Serial.print and Serial.println to write data
Here’s a complete program that writes “Hello world!” once very 500 ms.
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // opens serial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
}
void loop() {
Serial.println("Hello world!");
delay(500);
}Step 3: Open ‘Serial Monitor’ in the Arduino IDE
Finally, to view the incoming serial data, open up the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE.
And you should see something like this:
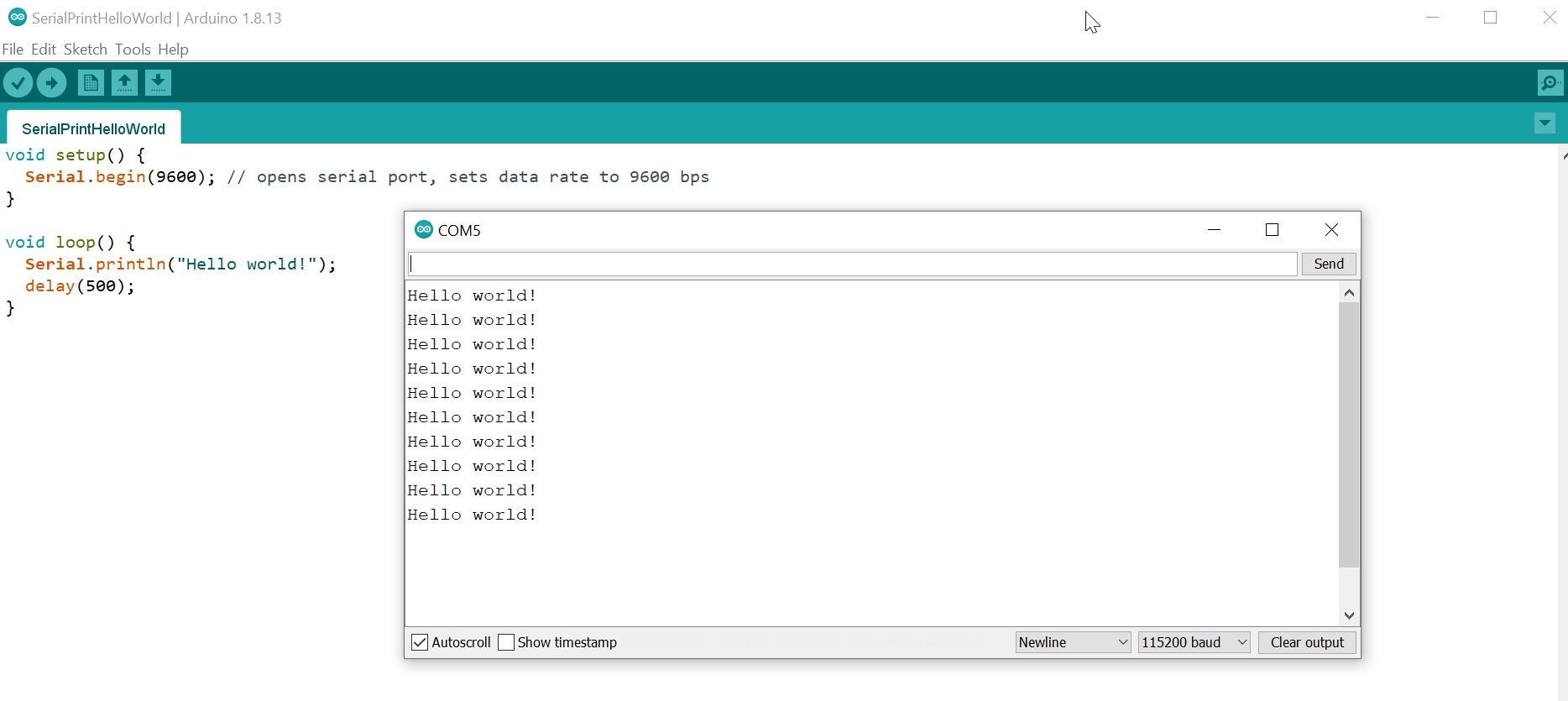
The full code is on GitHub here.
Printing out variables
You will obviously want to print out more than just strings. So, how do you print out variables?
The simple answer is to use multiple Serial.print and Serial.println statements. To print variables, put the variable as the sole parameter (see below). A more complicated answer is available in our Inside Arduino guide. You can also see the example code on the Serial.print API page.
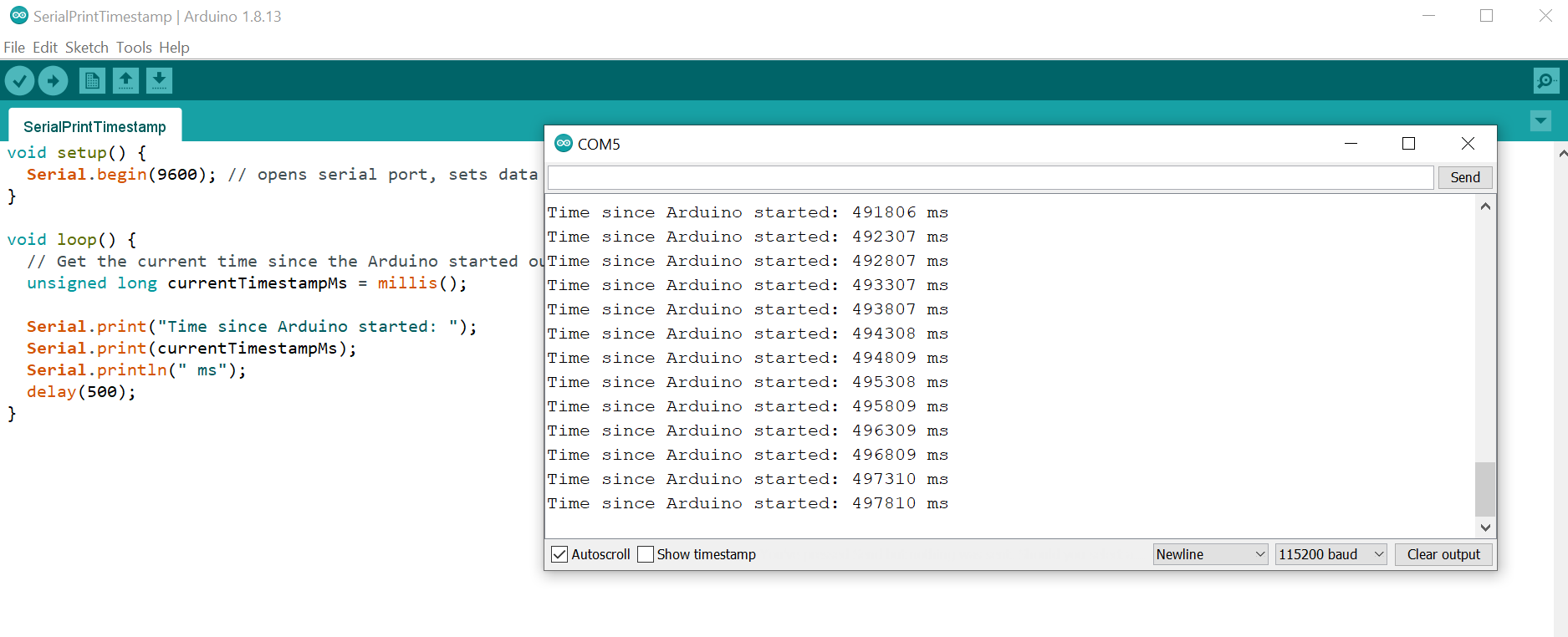
Below, we’ve written a simple program to print out the current time (in milliseconds) since the Arduino was turned on and our program began to run:
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600); // opens serial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
}
void loop() {
// Get the current time since the Arduino started our program (in ms)
unsigned long currentTimestampMs = millis();
Serial.print("Time since Arduino started: ");
Serial.print(currentTimestampMs);
Serial.println(" ms");
delay(500);
}
This code is also on GitHub here
Modify your blink code to use Serial.print
Now, let’s return to our blink code and modify it to use Serial.print to print out when the LED is on and off. Here’s my example.
Video. A video of the blink program with serial prints (source code).
Use the built-in LED
In addition to Serial.print, we can also use the Arduino’s built-in LED for some quick debugging (e.g., turn on the built-in LED to indicate some program state without hooking up an external LED circuit). On the Arduino Uno and Leonardo, the built-in LED is on Pin 13. So, if you write digitalWrite(13, HIGH); in your code, the built-in LED will turn on. Because not all Arduino boards have the built-in LED at Pin 13, you should use the constant LED_BUILTIN rather than a literal pin number.
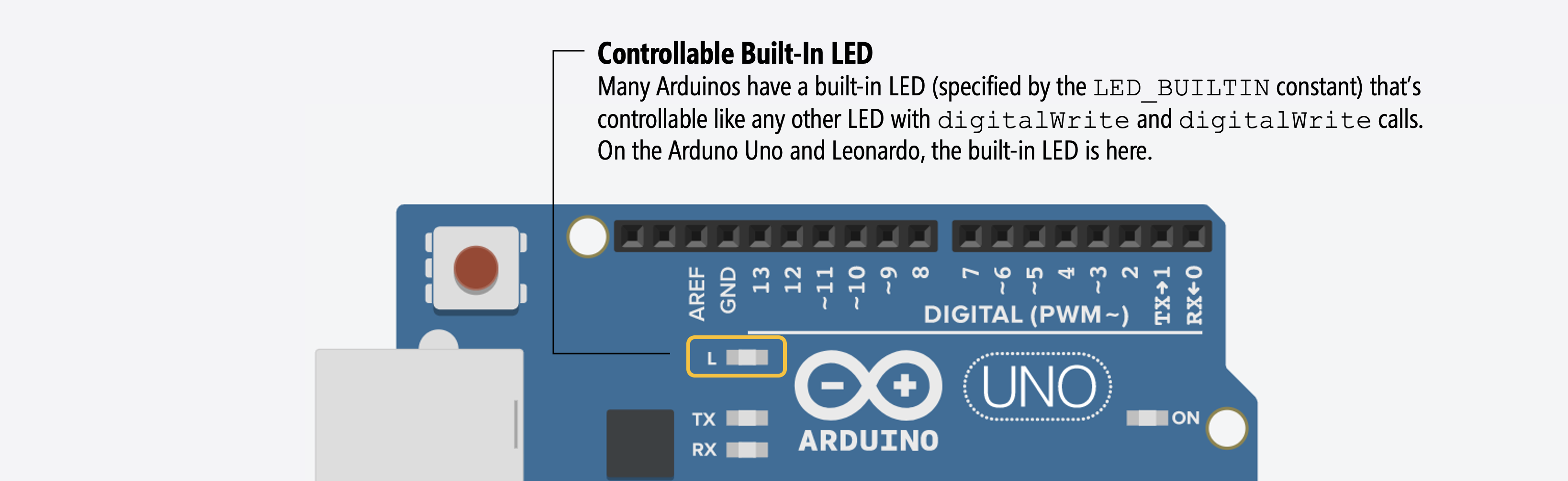
In fact, the official Arduino Blink example uses the built-in LED and the constant LED_BUILTIN to demonstrate blinking. This is also the program that ships with your Arduino and runs when you first power it up.
// the setup function runs once when you press reset or power the board
void setup() {
// initialize digital pin LED_BUILTIN as an output.
pinMode(LED_BUILTIN, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(1000); // wait for a second
digitalWrite(LED_BUILTIN, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(1000); // wait for a second
}You can access this example directly in the Arduino IDE:
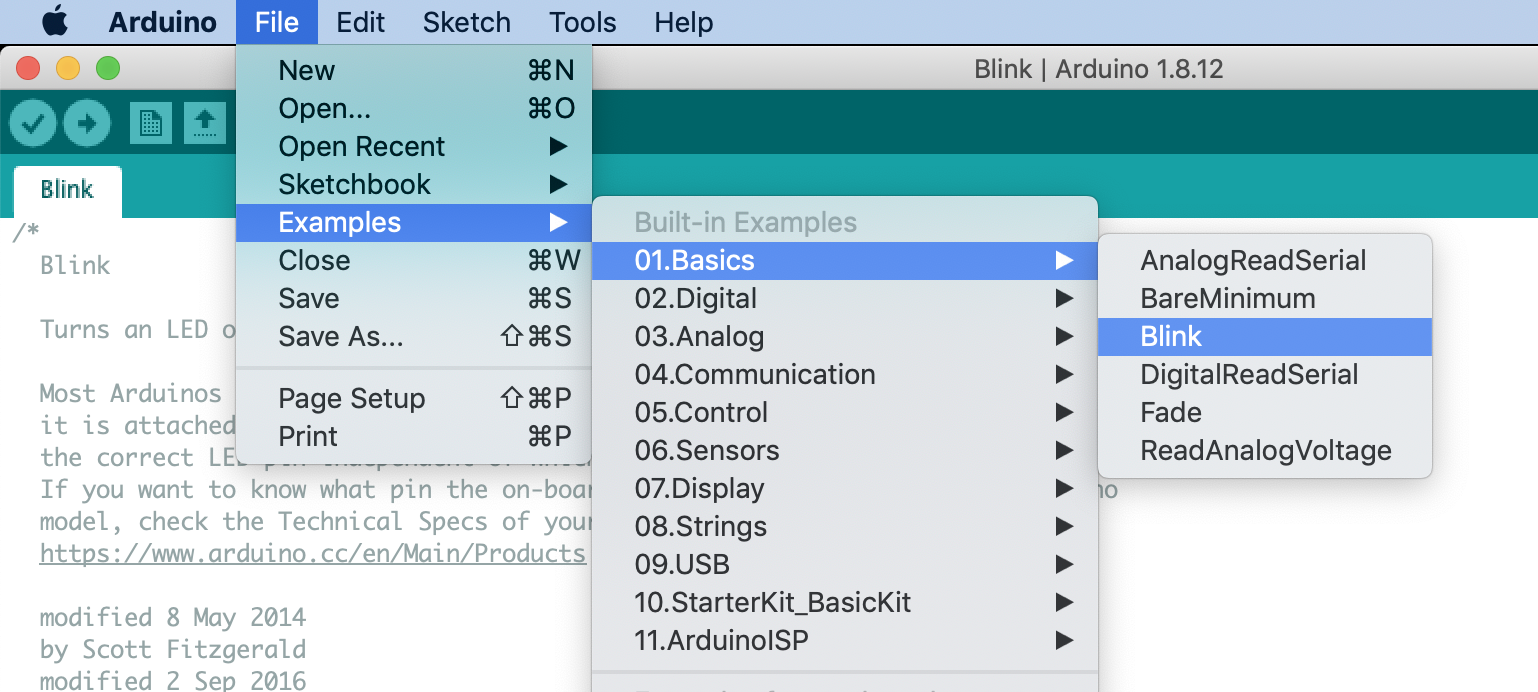
Next Lesson
Now that we know a bit about debugging and Serial.print(), it’s time to learn about “analog output” on the Arduino. We’ll be using Serial.print() throughout the rest of our tutorials.
Previous: Turning on an LED with Arduino Next: Fading an LED with Arduino