ESP32
Table of Contents
- Lesson 1: Introduction to the ESP32
- Lesson 2: Blinking an LED
- Lesson 3: Fading an LED with PWM
- Lesson 4: Analog Input
- Lesson 5: Playing Tones
- Lesson 6: Capacitive Touch Sensing
- Lesson 7: Internet of Things
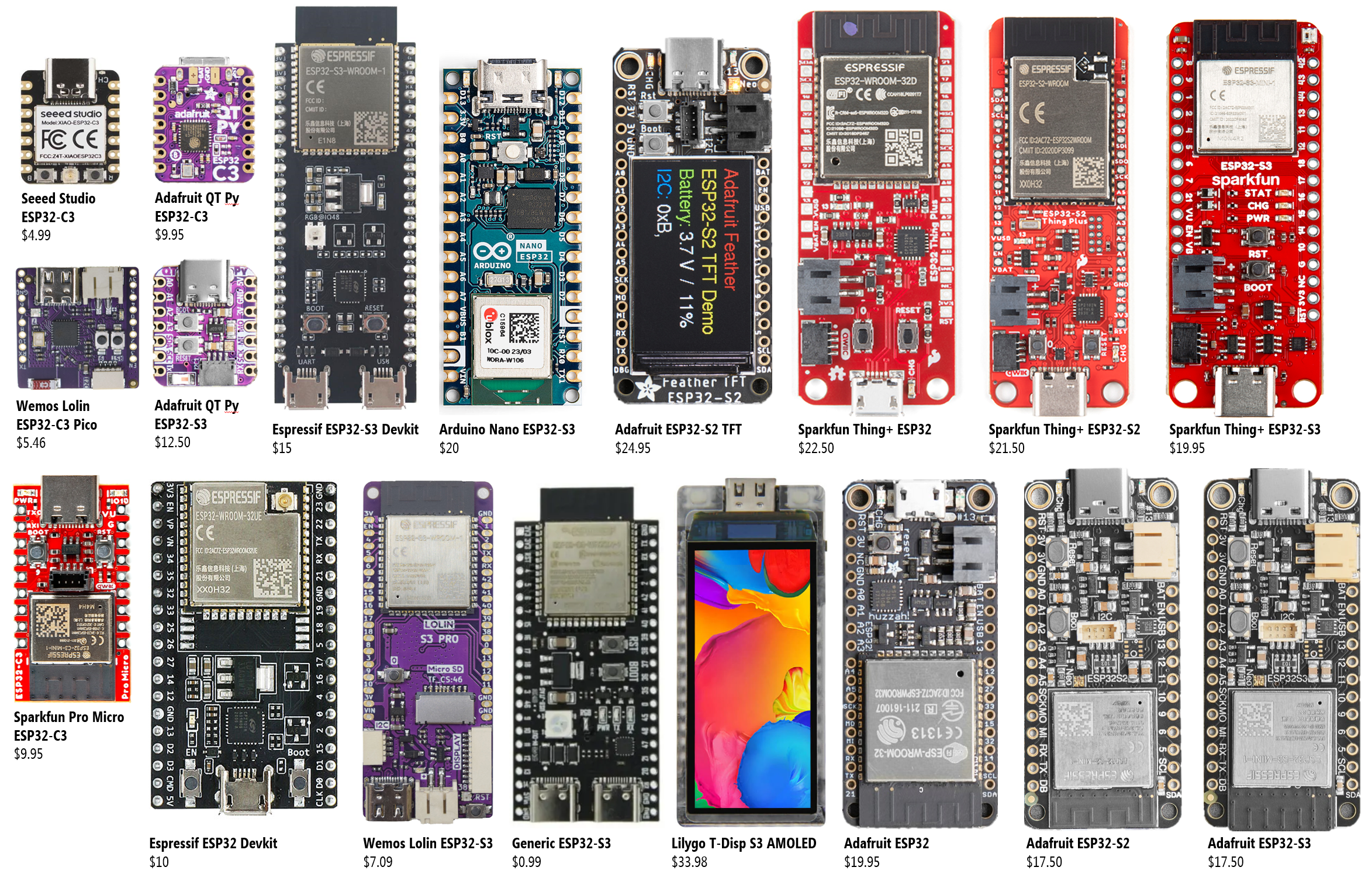 Figure. The ESP32 has quickly become the platform to learn and use for IoT projects. The ESP32s are fast, have WiFi and Bluetooth, and many are around $10 USD! And the best part is: you can program them with Arduino! So, all of your learning from previous lessons can be applied here!
Figure. The ESP32 has quickly become the platform to learn and use for IoT projects. The ESP32s are fast, have WiFi and Bluetooth, and many are around $10 USD! And the best part is: you can program them with Arduino! So, all of your learning from previous lessons can be applied here!
These tutorials are interactive and designed to be completed in order. All ESP32 code is open source and in this GitHub repository.
If this is your first time on our website, welcome 👋🏽! The following ESP32 lessons assume that you have completed both our Intro to Electronics and Intro to Arduino tutorial series. While not absolutely necessary, we recommend you start there!
Lesson 1: Introduction to the ESP32
In this lesson, you’ll learn about the ESP32, how it differs from and relates to the Arduino platform, and how to program and use the Huzzah32 ESP32 board.
Lesson 2: Blinking an LED
Introduces how to program the ESP32 using the Arduino IDE and ESP32 Arduino library (link)
Lesson 3: Fading an LED with PWM
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to use PWM output on the ESP32 to fade an LED on and off. The ESP32 Arduino library does not have an analogWrite method, so you’ll learn how to use PWM via an alternative method.
Lesson 4: Analog Input
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to use analog input on the ESP32 by building a potentiometer-based LED fader.
Lesson 5: Playing Tones
Arduino’s tone() method is not supported on the ESP32. In this lesson, you’ll learn how to play tones using the ledcWriteTone and ledcWriteNote in esp32-hal-ledc.c.
Lesson 6: Capacitive Touch Sensing
The ESP32 has built-in circuitry and software for capacitive touch sensing (docs). In this lesson, we’ll use the touch sensing functionality to turn on an LED.
Lesson 7: Internet of Things
The ESP32 is exciting not just because of its speed, memory, and GPIO capabilities but also because it is truly a modern Internet of Things (IoT) board with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth support. In this lesson, we’ll learn how to use WiFi and the IoT platform Adafruit IO to upload sensor data in real-time.